Table of Contents
Hair loss is a common problem that affects many people, especially as they age. It can be caused by various factors, such as genetics, hormones, stress, illness, medication, or environmental factors. Hair loss can have a negative impact on one’s self-esteem, confidence, and quality of life.
Fortunately, there are different medications and remedies that can help treating hair loss and promote hair growth. Some of them are approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), while others are natural or alternative options. In this article, we will explore some of the most effective and popular medications and remedies for treating hair loss.
Medications for treating Hair Loss

Medications are one of the most common and widely used treatments for hair loss. They work by preventing further hair loss, stimulating new hair growth, or both. However, they may not work for everyone or for every type of hair loss. They may also have some side effects or limitations that need to be considered.
Some of the most popular medications for hair loss are:
Minoxidil
Minoxidil is one of the most popular and widely used medications for hair loss. It is available over the counter in liquid, foam, and shampoo forms. It is applied topically to the scalp once or twice a day.
Minoxidil is approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) as a treatment for androgenetic alopecia (also known as male pattern baldness or female pattern hair loss) and alopecia areata (an autoimmune condition that causes patchy hair loss). It can also be used off-label for other types of hair loss, such as telogen effluvium (a temporary form of hair loss due to stress or illness) or traction alopecia (a form of hair loss due to excessive pulling or styling).
Minoxidil works by dilating the blood vessels in the scalp, which improves the blood flow and nutrient delivery to the hair follicles. This can stimulate the hair follicles to enter the active growth phase (anagen) and produce thicker and longer hairs. Minoxidil can also prolong the anagen phase and delay the transition to the resting phase (telogen), which can reduce hair shedding.
According to a systematic review of 19 studies published in 2019, minoxidil was found to be more effective than placebo or other treatments (such as finasteride or ketoconazole) in increasing hair count, hair thickness, and patient satisfaction1.
However, minoxidil is not a cure for hair loss and it does not work for everyone. The results may vary depending on the cause and severity of hair loss, the age and health status of the user, the lifestyle habits of the user, and the quality and quantity of minoxidil used.
Minoxidil may also cause some side effects, such as scalp irritation, dryness, itching, flaking, redness, burning, or allergic reactions. In rare cases, minoxidil may cause systemic effects, such as low blood pressure, fast heart rate, chest pain, headache, dizziness, fainting, or unwanted hair growth on the face or body.
Minoxidil is not recommended for pregnant or breastfeeding women, children under 18 years old, or people with scalp infections, wounds, or inflammation. Minoxidil may also interact with some medications, such as blood pressure drugs, anticoagulants, or topical corticosteroids.
Minoxidil is relatively affordable compared to other treatments for hair loss. The average cost of minoxidil in the United States ranges from $10 to $40 per month, depending on the brand, concentration, and form of the product.
Finasteride
Finasteride is another common and effective medication for hair loss. It is a prescription drug that is taken orally once a day. It is also available in a few prescription products that are applied topically.
Finasteride is approved by the FDA as a treatment for androgenetic alopecia in men only. It is not approved for women or children. Finasteride can also be used off-label for other types of hair loss, such as alopecia areata or cicatricial alopecia (a rare type of hair loss that involves scarring of the scalp).
Finasteride works by inhibiting the enzyme 5-alpha-reductase, which converts the hormone testosterone into dihydrotestosterone (DHT). DHT is a potent androgen that can bind to the androgen receptors in the hair follicles and cause them to shrink and produce thinner and shorter hairs. By reducing the levels of DHT in the scalp, finasteride can prevent or slow down the miniaturization of the hair follicles and stimulate new hair growth.
According to a 2018 study, finasteride can be used to slow hair loss and help stimulate new hair regrowth in men with androgenetic alopecia2.
However, finasteride is not a cure for hair loss and it does not work for everyone. The results may depend on several factors, such as the dose and duration of treatment, the age and health status of the user, the genetic susceptibility to DHT, and the compliance and adherence to the medication.
Finasteride may also cause some side effects, such as decreased sex drive, erectile dysfunction, ejaculation problems, breast tenderness or enlargement, or depression. In rare cases, finasteride may cause serious effects, such as liver damage, prostate cancer, or male breast cancer.
Finasteride is not recommended for pregnant or breastfeeding women, children, or people with liver disease, prostate cancer, or urinary problems. Finasteride may also interact with some medications, such as antifungal drugs, antidepressants, or blood thinners.
Finasteride is more expensive than minoxidil, but still affordable compared to other treatments for hair loss. The average cost of finasteride in the United States ranges from $20 to $80 per month, depending on the brand, dose, and insurance coverage.
Spironolactone
Spironolactone is a medication that is mainly used to treat high blood pressure, heart failure, or fluid retention. However, it can also be used off-label to treat hair loss, especially in women with androgenetic alopecia or hirsutism (excessive hair growth on the face or body).
Spironolactone is a prescription drug that is taken orally once or twice a day. It is also available in some topical products that are applied to the scalp.
Spironolactone works by blocking the action of androgens, such as testosterone and DHT, on the hair follicles. Spironolactone can also reduce the production of androgens in the adrenal glands and ovaries. By lowering the levels of androgens in the scalp, spironolactone can prevent or slow down the hair loss and stimulate new hair growth.
According to a 2015 study, spironolactone can be used to improve hair density and quality in women with androgenetic alopecia3.
However, spironolactone is not a cure for hair loss and it does not work for everyone. The results may vary depending on the dose and duration of treatment, the age and health status of the user, the hormonal balance of the user, and the cause and type of hair loss.
Spironolactone may also cause some side effects, such as low blood pressure, high potassium levels, irregular periods, breast tenderness or enlargement, or fatigue. In rare cases, spironolactone may cause serious effects, such as kidney damage, liver damage, or bleeding.
Spironolactone is not recommended for pregnant or breastfeeding women, men, children, or people with kidney disease, liver disease, or adrenal insufficiency. Spironolactone may also interact with some medications, such as blood pressure drugs, diuretics, potassium supplements, or NSAIDs.
Spironolactone is relatively cheap compared to other treatments for hair loss. The average cost of spironolactone in the United States ranges from $10 to $30 per month, depending on the brand, dose, and insurance coverage.
natural remedies for treating hair loss that you can try at home
- Massage your scalp with a hair oil, such as coconut oil, to stimulate blood flow and nourish the hair follicles. This can help improve hair growth and thickness1.
- Apply aloe vera gel to your scalp and hair to moisturize and condition them. Aloe vera can also reduce inflammation and dandruff, which can contribute to hair loss2.
- Apply onion juice to your scalp and hair to boost hair growth. Onion juice contains sulfur, which can increase collagen production and strengthen the hair strands. Onion juice can also fight bacteria and fungi that can cause scalp infections and hair loss2.
- Apply rosemary oil to your scalp and hair to stimulate hair growth and prevent hair loss. Rosemary oil can improve blood circulation, reduce inflammation, and prevent the conversion of testosterone to DHT, which is a hormone that can shrink the hair follicles and cause hair loss2.
- Apply lemon juice or oil to your scalp and hair to enhance hair quality and growth. Lemon can provide vitamin C, which is essential for collagen synthesis and hair health. Lemon can also cleanse the scalp and remove excess oil and dirt that can clog the hair follicles and cause hair loss2.
These are some of the natural remedies that you can try for hair loss, but they may not work for everyone or for every type of hair loss. You should consult with a doctor or a dermatologist before using any of these remedies, especially if you have any medical conditions or allergies. You should also do a patch test before applying any of these remedies to your scalp and hair to check for any adverse reactions.
Other ways for treating hair loss
- Microneedling, a technique that creates tiny punctures in the scalp to stimulate healing and absorption of the plasma. Microneedling can be combined with PRP or other topical products to enhance the outcome.
- Laser hair restoration, a treatment that uses low-level laser light to stimulate blood flow and cellular activity in the scalp. Laser hair restoration can improve hair density, thickness, and quality.
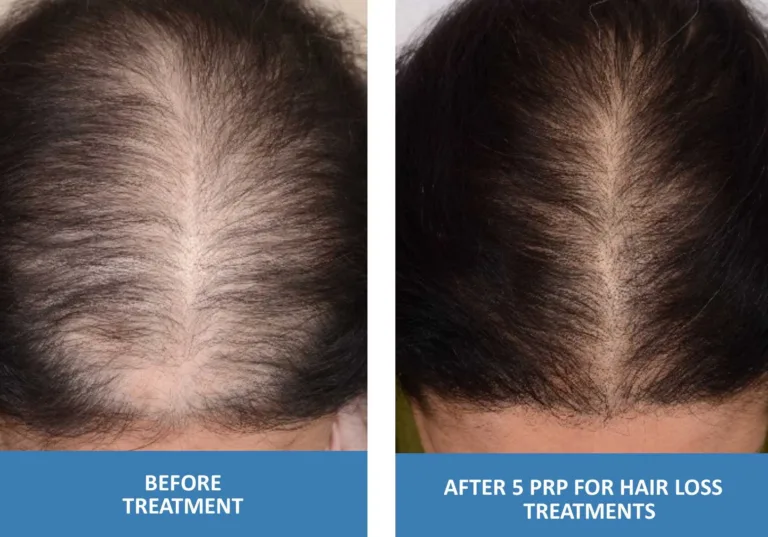
- PRP, it works by stimulating the dormant hair follicles (the structures that produce hair) in your scalp to enter the active growth phase (anagen). This can result in increased hair density, thickness, and length over time and in this article you can read more about it “The Magic of Platelet-Rich Plasma: PRP For Treating Hair Loss, the most 5 FAQs“
- Hair transplant, is a surgical procedure that involves moving hair follicles from one area of the scalp (donor site) to another area (recipient site) where hair is thinning or missing. Hair transplant can be used to treat some forms of alopecia, such as androgenetic alopecia and cicatricial alopecia, but not others, such as alopecia areata and in this article you can read more about it “Hair Transplant for Treating Alopecia: 4 things you should Know“.
These are some of the alternative treatments for hair loss that you can consider, but they may not work for everyone or for every type of hair loss. You should consult with a doctor or a dermatologist before using any of these treatments, especially if you have any medical conditions or allergies. You should also do a patch test before applying any of these treatments to your scalp and hair to check for any adverse reactions.
Conclusion
Hair loss is a common problem that can be treated with various medications, such as minoxidil, finasteride, or spironolactone. These medications can help reduce hair loss or stimulate new hair growth, or both. However, they are not suitable for everyone and they may have some side effects or limitations.
Therefore, it is important to consult with a doctor or a dermatologist before using any medication for hair loss. They can help you diagnose the cause and type of your hair loss, prescribe the best medication for your condition, monitor your progress and response, and adjust your treatment plan as needed.